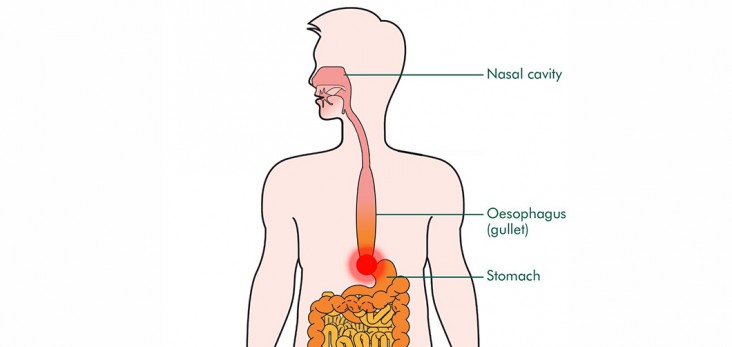
Esophageal Manometry is a procedure which is used to identify various pathological conditions associated with the esophagus (food pipe) and lower esophageal sphincter (LES), the valve like ring of muscle, located between the esophagus and stomach. This valve is responsible in controlling the movements taking place when food bolus is passed through the esophagus to the stomach and improper functioning of it can result in condition like acid reflux or gastro esophageal reflux disease (GERD).
Patients who present with symptoms such as acid regurgitation, heart burn, chest pain (which mimic heart attack), difficulty or pain in swallowing, nausea and vomiting can be advised to go for esophageal manometry. It is also done Prior to anti reflux surgery.
Before esophageal manometry eight hour or over-night fasting is advised by the Gastroenterologist. In addition to that, a complete history including current medications and past surgical history will be taken from the patient where certain drugs like calcium channel blockers, nitrates, nitroglycerin and sedatives might have to be withdrawn for a certain duration.
Patient will be lied down on bed, and an application to numb the nasal canal (anesthetized) is applied which will help in reducing the discomfort throughout the procedure.
Thereafter, a very thin and flexible tube is inserted into the nose which will pass down the esophagus until it reaches the stomach and when it is pulled back gradually, the patient is asked to swallow at different points so that the individual pressures and tone of the esophageal muscles and lower esophageal sphincter is measured by sensors attached to the tube. This test is also used to measure the pH value of the esophageal contents with the help of the pH probe attached to the same tube.
This whole procedure takes approx 30 to 45 minutes.
It is normal that some patients may gag or feel uncomfortable when the tube is inserted initially and get a stuffy nose during the procedure. However, breathing is not interfered by the procedure.
Major complications of esophageal manometry include perforation, where a trauma to the esophagus might have caused a hole on it resulting in leakage and aspiration where an inhalation of saliva or some other contents in the stomach takes place which can give rise to pneumonia and lung injuries.
The results obtained by esophageal manometry will help to diagnose problems such as abnormal contractions of esophageal muscles, Achalasia cardia (improper opening of LES), Hiatus Hernia and GERD (weak LES), spasmodic movements of the esophagus and Scleroderma (an autoimmune condition which will paralyze muscles of esophagus).
Methods of treatment will be planned based on the type and severity of the conditions diagnosed by esophageal manometry.
Esophageal Manometry is useful test to diagnose food pipe movement and pressure disorders and is available at colorectal department of Fortis Hiranandani hospital Vashi , Navi Mumbai, headed by Dr Nitish Jhawar.