What is meant by a laparoscopy?
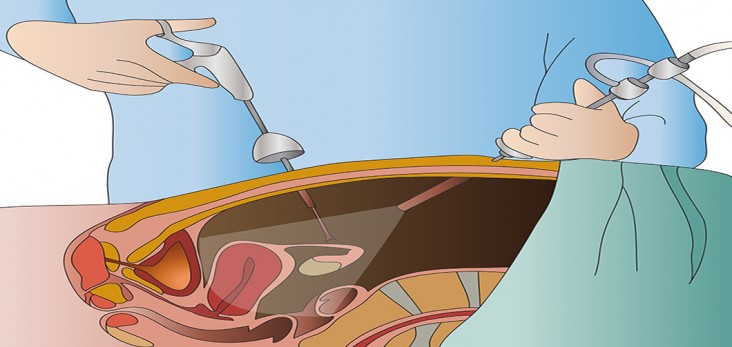
Also known as Key-hole surgery, laparoscopy is a mode of surgical intervention on patients who have been diagnosed with different conditions in the abdomen or pelvis. This procedure allows the surgeon to visualize the inner aspect of the abdomen and pelvis using laparoscope without creating a large incision on the skin for its diagnostic access.
More importantly, laparoscopy is used to carry out various additional surgeries and procedures other than simple visualization, where the surgeon could connect numerous instruments to the laparoscope and excise or trim tissues, take out tissue samples known as biopsies, grasp organs whenever necessary. Being a minimally invasive surgery, laparoscopy has been accepted world-wide as a very effective surgical intervention preferred by health professionals as well as patients over extensive open surgeries.
Laparoscopy is vastly used in the aspects of gynecology and obstetrics, gastroenterology and urology which mainly deals with pathological conditions related to organs lying inside the body.
Most common surgeries carried out using this latest technology include, gall bladder removal (laparoscopic cholecystectomy), Removal of the appendix (appendicectomy), Hernia Repair, Fundoplication, removal of the ectopic endometrial tissues (in Endometriosis), removal of various part of the bowel, female sterilization, surgical intervention for ectopic pregnancy, biopsy samples in suspected cases of malignancy etc.
Most of the Laparoscopic surgeries are carried out under general anesthesia so that the patient will be unconsciousness and pain free throughout the surgery. The surgeon will then make one (single-incision or single port laparoscopy) or few tiny incisions on the abdomen using a special needle.
Through a small flexible tube Co2 gas is pumped inside. This gas is very much useful to push bowel away from the operative site, in order to make a clear visualization. Laparoscope is inserted inside abdomen through tiny hole.
Once the procedure is over, the gas is pumped out, the incision is sutured and a dressing is put on.Some patients will be discharged on the same day after wearing off of anesthesia while others will be kept for monitoring for 24 hours depending on the post-operative condition of the patient and type of surgery.
Complications of laparoscopic surgeries are quite rare but there can be mild bleeding or bruising at the site of excision, accidental trauma to the organs inside the abdomen resulting in perforation (generalized sepsis) which might need emergency laparotomy or open abdomen surgery, general complications of anesthesia and wound infections which might need antibiotics. The incidence of these complications will vary according to the type of surgery carried out and comorbidities of the patient.
However, despite of all the complications reported, Laparoscopy is still preferred over open surgeries due to its minimal invasive nature, negligible pain post operatively, shorter duration of hospital stay, quick recovery and comparatively small scar.