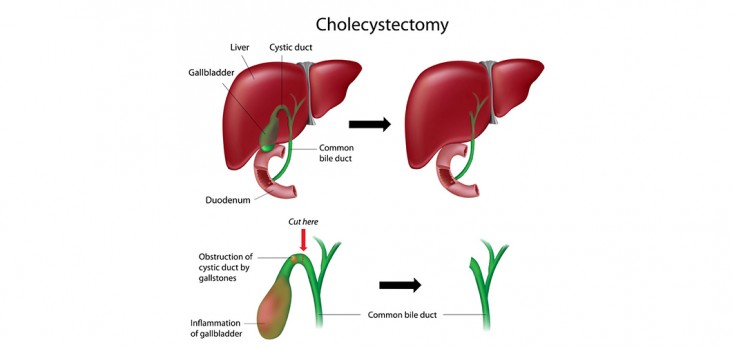
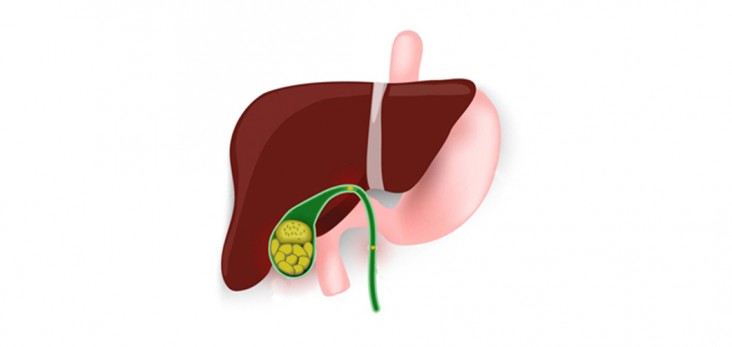
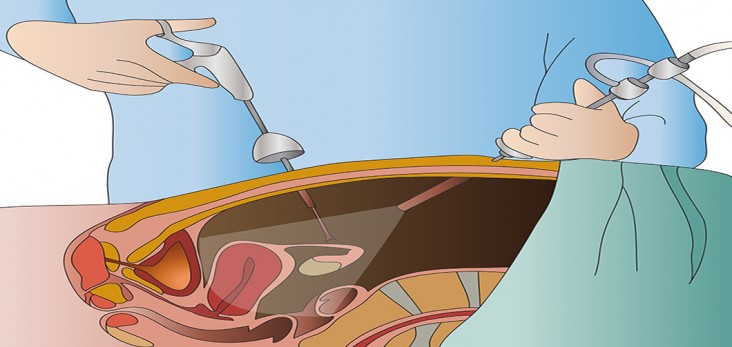
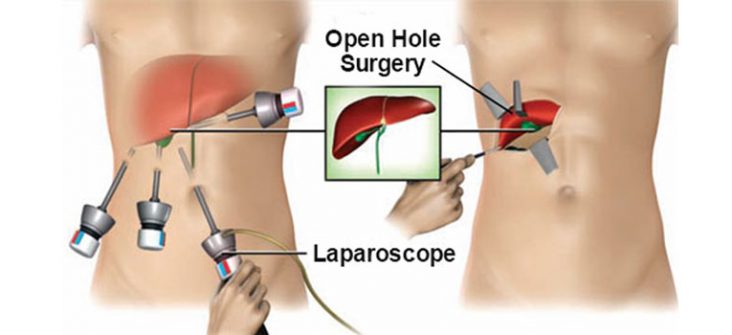
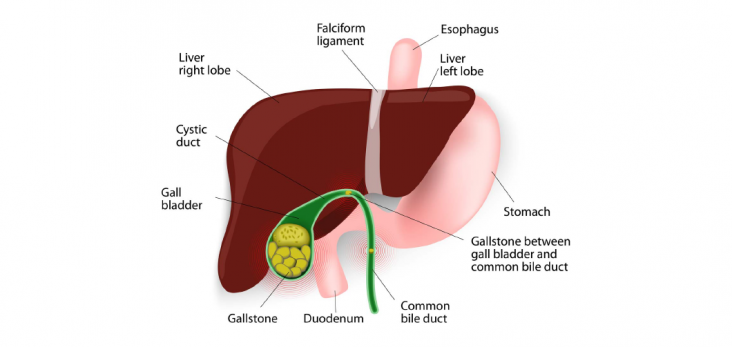
Laparoscopic gallbladder surgery (cholecystectomy) removes the gallbladder and gallstones through several small cuts (incisions) in the abdomen. The surgeon inflates patient’s abdomen with air or carbon dioxide in order to see clearly.
Sometimes patients are nauseated after waking from the anesthesia. This sensation usually passes. If it does not, medication can be given to relieve it.
Postoperative pain can usually be controlled with over-the-counter pain relievers. Some patients may need a stronger, prescription analgesic.
The incisions are covered by small adhesive bandages that can be removed in about 5 days and the stitches dissolve over time. The area must be kept dry until the wound begins to heal and sponge baths are recommended for the first day or two.
Recovery from the laparoscopic procedure is quicker than from the open procedure. As the anesthesia wears off, and once vital signs stabilize, the nurse offers the patient ice chips. If ice is tolerated, water and other clear liquids are offered. Once liquids are tolerated, patients can eat a light meal and the IV is removed.
How is it different from an open surgery?
Recovery from open surgery is not as rapid. Patients experience pain at the incision site and a narcotic pain reliever is usually required for the first day or two. The patient may not be able to eat until the morning after surgery. The intravenous is left in until food and fluids are taken and tolerated.
Patients are usually able to get out of bed by the next morning. It is important to get up and walk as soon as possible to help blood circulation return to normal and to avoid complications such as blood clots. The hospital stay generally lasts 3 to 7 days and it usually takes about 3 weeks to fully recover. This procedure leaves a large abdominal scar, which may fade over time…
Diet instructions you need to know after the surgery
When you consider about your diet after the gallbladder surgery. No need to follow a special diet after having the surgery, as the gallbladder isn’t essential for digestion. You can usually start eating normally a few hours after your operation, although you’ll probably prefer to eat small meals to start with.
You may have been advised to follow a low-fat diet for several weeks before surgery, but this doesn’t need to be continued afterward. Instead, you should aim to have a generally healthy, balanced diet (including some fats).
Conclusion
Even Though cholecystectomies are safe, but complications can develop. The main disadvantage of laparoscopic surgery has increased the risk of injury to the bile duct, which connects the gallbladder and the liver. This rarest complication can cause serious liver damage.
If you experience side effects from the surgery – including indigestion, bloating, flatulence or diarrhea – it may help to make some small adjustments to your diet such as
- Avoid drinks containing caffeine – such as coffee and tea,
- Avoid foods that make the problems worse – such as spicy or fatty foods,
- Gradually increase your intake of fibre – good sources of fibre include fresh fruits and vegetables, wholegrain rice, whole-wheat pasta and bread, seeds, nuts, and oats.